Predicate Adjective
A predicate adjective follows a linking verb and describes or gives more detail about the subject.
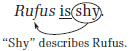
In the sentence above, the word "shy" describes "Rufus"— shy Rufus.
In the sentence above, the word "lonely" describes "Lulu"— lonely Lulu.
The linking verb that connects the subject to the predicate noun or adjective may be a "to be" verb (is, am, are, was, were, be, been), but other linking verbs such as become, seem, feel, appear, look, taste, and smell also can serve as linking verbs.
Lulu looks sad.
The lemon tastes sour.
Freshly baked bread smells good.
Identifying Predicate Adjectives
To discover how the predicate functions, we can replace a possible linking verb with a "to be" verb. Consider the following sentence:
Lulu looks sad.

In the sentence above, we see that "sad" describes the subject "Lulu"— sad Lulu. Therefore, the predicate word "sad" is an adjective.
Now consider this sentence:
The lemon tastes sour.
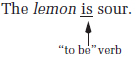
In the sentence above, we see that "sour" describes the subject "lemon"— sour lemon. The predicate word "sour" is an adjective.
Now consider this sentence:
Freshly baked bread smells good.
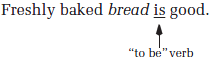
In the sentence above, we see that "good" describes the subject "bread"— good bread. The predicate word "good" is an adjective.
Compounds
We often see compound (more than one) expressions, as in the sentences below.
Examples
Write each predicate adjective that you find in the sentences below.
- Some amphibians look scary.
- Wyoming seems high and windy.
- These squirrels are arboreal.
- I wonder if that monkey is tame.
- The family's small business appears profitable.
- Missing some ingredients, the pie tasted odd.
- Before the exam, Dan felt nervous.
- After the test, we all felt elated.
- Miss Yu, the librarian, was friendly and helpful.
- The dog's eyes looked glassy and droopy.
Solutions
- scary
- high, windy
- arboreal
- tame
- profitable
- odd
- nervous
- elated
- friendly, helpful
- glassy, droopy